Radiotherapy is a prevalent treatment modality for thoracic tumors; however, it can lead to radiation-induced lung injury (RILI). To date, the pathogenesis of RILI remains elusive. Research has shown an association among radiation-induced pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, and NLRP3 inflam-masome activation. ACT001, a prodrug of micheliolide, has been demonstrated can effectively suppresses the production of the NLRP3 inflammasome and proinflammatory cytokines, but its impact on RILI requires further validation.
CIRP developed a novel strategy to investigate the radioprotective effects of ACT001 on RILI and elucidate its underlying mechanism. The results demonstrated that ACT001 ameliorated RILI, diminished pro-inflammatory cytokine release and fibrosis, and mitigated the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome while inhibiting pyroptosis in lung tissue. The study reveals its potential as a novel protective agent for RILI. The precise mechanism of this protective effect remains to be elucidated and warrants further investigation.
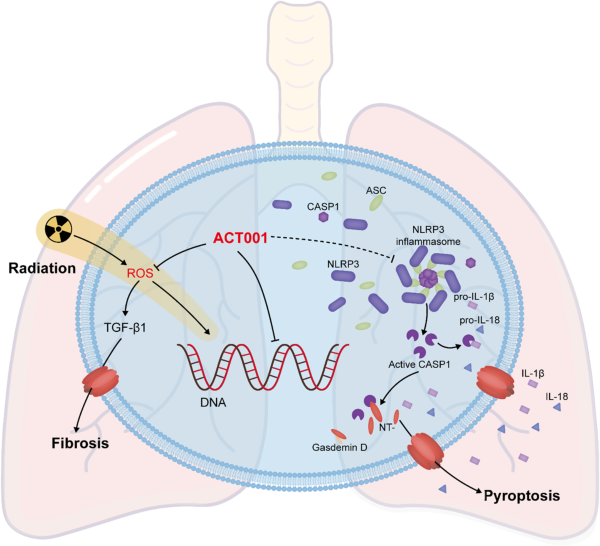
The mechanism through which ACT001 mitigates RILI
Contact:official@cirp.org.cn



 打印
打印



